| Home | About Us | Resources | Archive | Free Reports | Market Window |
|
Steve's note: Mark Ford, editor of The Palm Beach Letter, recently wrote a guide for his readers on dealing with debt. We've excerpted a part of that below. Before you read it, you should know Mark himself started with no money. He was the son of a teacher – one of many children. He built a multimillion-dollar fortune himself... and learned his lessons about wealth and debt exactly as he describes... A Self-Made Millionaire's Guide to Dealing with DebtBy
Saturday, December 10, 2011
I had my first serious run-in with debt when I was 30 years old.
My wife K and I were renting a condominium in Washington, D.C. Our landlady came to us with an exciting opportunity: We could buy the condo for $60,000 with no money down. For just $100 a month more than what we were already paying for rent, we would be paying a mortgage. It sounded like a great deal, so we took it.
What we bought was a negatively amortizing mortgage with a three-year term and an 11% interest rate. That meant, every three years we were paying $19,800 in debt service and another $3,000 in closing costs.
We didn't realize what was going on because our monthly payments were only $550. I was too foolish then to ever ask myself, "What is the cost of this debt?"
I tried to find another bank to take me out of this scam but none would. The mortgage we had signed was not backed by the government (Freddie Mac/Fannie Mae), which meant that no other bank would touch it.
I learned that when banks make it easy to borrow money, it's not because you are a nice, deserving person. I learned that if you can get a loan despite poor credit (as ours was at the time), there is usually a scam involved. It also taught me to always ask the two critical questions about debt, "How much will it cost?" and, "Can I afford it?" It was an expensive lesson.
Many of us view debt as a necessity. We buy homes with it. And cars. And boats, and toys, and vacations. Some use it to buy the basics: clothes, food, and furniture.
Debt is not necessary. It is a luxury. Sometimes debt is useful. Sometimes it is wasteful. But debt is always dangerous.
It is unnecessary because there are always less expensive ways of getting what you want. And it is dangerous because it can sometimes be very expensive.
Let me give you two examples.
Let's say that, like most Americans, you are in the habit of buying things with credit cards. After a while, you notice that you have accumulated $30,000 in total debt. You decide to cut up your cards and repay your debt. You can devote $400 a month to paying it back. How long will it take, and how much will it cost you?
The answer may surprise you. Assuming an interest rate of 10%, it will take you 10 years to pay off the credit card debt. And your total payments will be $47,275. Of that, $17,275 will have been in interest payments.
Or let's take a $150,000 home on which you take a $120,000 loan with a 6.5% interest rate over 20 years. The mortgage payments are $894 a month, which you can afford. But how much will that house really cost you? Including interest payments? You will end up paying $244,725 for that house. Almost 40% of that – $94,725 – will have been to interest payments.
The commercial community (bankers and manufacturers) doesn't want you to be afraid of debt. And neither does the government. These institutions want you to like debt. They want you to use it. They want you to go into debt because it is good for them.
When you take out a mortgage to buy a home, or sign a lease on a car, or use credit cards to pay for your lifestyle expenses, the commercial community profits. The manufacturers make money on products you may or may not need. And the banks make money on your debt.
The mainstream financial media rarely talks about the dangers of debt. That's because they make their profits from the financial institutions and manufacturers whose advertisements support their publications.
And the government actually encourages its citizens to take on debt. This was the recommended strategy for getting us out of the Great Recession that the (second) Bush administration (and the Federal Reserve) advocated and it's the same scheme that Obama's people are advocating today.
Here's what you should know about debt:
As a general rule, you should live without it. You should find less expensive ways to acquire the things you need.
Unless you are wealthy, don't lease your car. Buy it. Buy the car you can afford, not the car you believe will make you happy. Any non-appreciating asset (such as a car) will never make you happy if you have to pay its debt service. I didn't buy my first luxury car until I was a multimillionaire.
Don't buy anything with a credit card. Keep only one credit card for renting cars. Use a debit card to buy clothes and groceries. If you don't have enough money in your bank account to use your debit card on a purchase, don't buy it. If you don't have enough money in the bank to buy something, it means you can't afford it.
If you can't afford the debt on your house, sell it (if you can) and buy something cheaper. In any case, start paying off the principle balance of your house (the amount you owe, not the interest you will owe) as fast as you can. Make it a goal to own your house free and clear as soon as possible.
If you have debt, pay it off as fast as you can, but not before you have filled up your bucket for emergency savings. By emergency savings, I mean money you will need to pay your bills if you lose your job. Six months' income is what some financial advisors recommend. I'd recommend a year. It may take you that long to replace your lost income.
Pay off your debt even if the interest rate is low. In theory, you should put your extra money elsewhere if you can earn more on it than you are paying in interest. If, for example, you can get 4% in municipal bonds and you have a student loan at 2%, it makes more sense to buy municipals bonds and pay your student loan off slowly. But in reality, the extra 2% you are earning on the spread is not worth the risk in carrying the debt.
When I started earning money, the first thing I did was get rid of that terrible loan on the condominium I told you about earlier.
The next thing I did was pay off the mortgage I took on a home. I paid it off in two or three years, even though it was a 30-year mortgage. I loved the idea of owning my home free and clear. So I put every extra dollar I had toward paying down that mortgage. The bank didn't like it, but the day I tore up that mortgage... I felt like I had been emancipated from financial slavery.
Finally, if you are troubled by debt, know this: you can get out of it just as I did.
Regards,
Mark Ford
Further Reading:
"The hardest part about freeing yourself from financial slavery is recognizing the chains that are binding you and deciding to do something serious about them," Mark says. If you're ready, don't miss Mark's two-step plan to downsizing your debt... and stepping out on the path to financial freedom. Get the details here: A Three-Year Plan to Achieve Financial Independence.
Mark recently sat down with our sister site The Daily Crux to discuss wealth, investment, and economics. What he says about government "stimulus" might offend you, but we guarantee he'll force you to challenge your beliefs... This interview is free to Crux readers. Access it here.
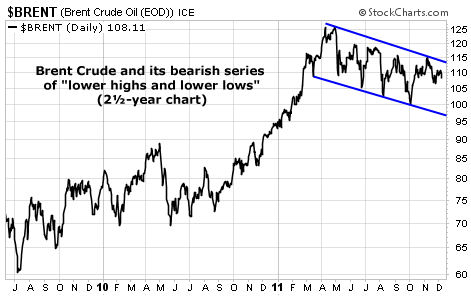
Market NotesCHART OF THE WEEK: THE GLOBAL OIL PRICE IS FALLING This week's chart offers a clue as to what "the market" is saying about the global economy right now. It concerns the oil price you never hear about...
Many Americans are familiar with our domestic "West Texas Intermediate" oil price. It's what commentators are referring to when they say, "Oil prices rose $2 per barrel today."
But a more accurate measure of what the world is paying for oil is the "Brent Crude" price. It's a better measure of what the growing markets of Asia are paying for energy. Over 60% of the global oil supply is priced in Brent... which is trading for around $108 per barrel right now.
As you can see from this week's chart, Brent enjoyed a big run higher in late 2010 and early 2011. Robust demand, central bank "goosing," and fears of political blowups in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) sent prices from $85 per barrel to $125 barrel. But over the past six months or so, Brent Crude has backed off its high... and put in a bearish series of "lower highs and lower lows." Should Brent continue this steady decline, it's a major signal the global economy is slowing down... or worse, hitting a wall.
 |
Stat of the week
42%
Increase in North Dakota's oil production in October versus the same time one year ago. It is on pace to become the country's second-largest oil-producing state in 2012 (just behind Texas).
In The Daily Crux
Recent Articles
|

